what is beta galactosidase|β : Tuguegarao Galactosidases are enzymes (glycoside hydrolases) that catalyze the hydrolysis of galactosides into monosaccharides. The galactosidases are categorized as either alpha or beta, according to the category of glycoside they hydrolyze.
There are many ways you can raise money to help St. Jude kids: Learn about the different ways you can fundraise Find an event; Create your own event; Or, call our Volunteer Service Centers at (800) 457-2444.
what is beta galactosidase,
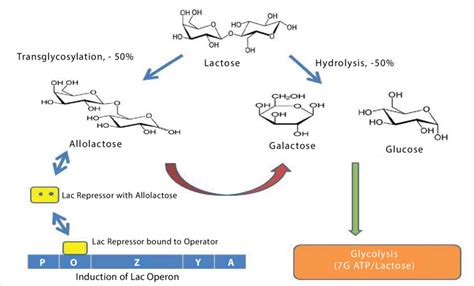
β-Galactosidase is an exoglycosidase which hydrolyzes the β- glycosidic bond formed between a galactose and its organic moiety. It may also cleave fucosides and arabinosides but at a much lower rate. It is an essential enzyme in the human body. Deficiencies in the protein can result in galactosialidosis or Morquio B syndrome.

Beta-galactosidase is a complex protein that exhibits a quaternary structure, typically forming a tetramer composed of four identical subunits. Each subunit is intricately folded, creating a three-dimensional conformation essential for its enzymatic activity.Beta-galactosidase is a powerful tool for genetic engineering of bacteria. Beta-galactosidase consists of four chains, each with 1023 amino acids (blue), that form four active sites. The substrate/product allolactose (pink and white) can be seen here in two of these active sites.
The main difference between lactase and beta galactosidase is that lactase is specialized for the hydrolysis of lactose specifically, while beta-galactosidase is a more versatile enzyme capable of breaking down a variety of galactoside compounds, including lactose. β-Galactosidase is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that possesses both hydrolytic and transgalactosylation properties and has several benefits and advantages in the food and dairy industries. The catalytic process of β-galactosidase involves the transfer of a sugar residue from a glycosyl donor to an acceptor via a double-displacement mechanism.

Galactosidases are enzymes (glycoside hydrolases) that catalyze the hydrolysis of galactosides into monosaccharides. The galactosidases are categorized as either alpha or beta, according to the category of glycoside they hydrolyze.what is beta galactosidase βGalactosidases are enzymes (glycoside hydrolases) that catalyze the hydrolysis of galactosides into monosaccharides. The galactosidases are categorized as either alpha or beta, according to the category of glycoside they hydrolyze.Beta-galactosidase is a lysosomal enzyme responsible for catalyzing the hydrolysis of gangliosides. Isolated deficiency of this enzyme can be expressed clinically as 2 different diseases, GM1 gangliosidosis (GM1) and Morquio syndrome B (MPS IVB: mucopolysaccharidosis IVB), or in some patients as a disease that combines the skeletal features of .Beta-galactosidase (B-gal for short) is an enzyme that will process the substrate lactose. In applications using B-gal as a reporter (lacZ gene), two lactose analogues are commonly used: X-gal or ONPG (as pointed out by @Alan Boyd).
what is beta galactosidase|β
PH0 · β
PH1 · What is the function of beta galactosidase?
PH2 · What is the Difference Between Lactase and Beta Galactosidase
PH3 · What are the advantages and disadvantages of using beta
PH4 · Molecule of the Month: Beta
PH5 · Galactosidases
PH6 · Beta
PH7 · BGA
PH8 · A Review on the Various Sources of β